Frame Transformations Example¶
Outline¶
Local coordinate transformations
World coordinate transformations
Loading frame information¶
This step is required to use the frame transformations class. The content of this snippet is explained in Notebook 1.
from vod.configuration import KittiLocations
from vod.frame import FrameDataLoader
kitti_locations = KittiLocations(root_dir="view_of_delft_PUBLIC",
output_dir="example_output",
frame_set_path="",
pred_dir="",
)
frame_data = FrameDataLoader(kitti_locations=kitti_locations,
frame_number="01201")
Coordinate systems¶
As mentioned in notebook 1, we recorded the output of the following sensors:
- ZF FRGen21 3+1D radar mounted behind the front bumper.
- Stereo camera mounted on the windshield.
- Velodyne HDL-64 S3 LIDAR scanner on the roof.
The location of these sensors with respect to the car are presented in the figure below:
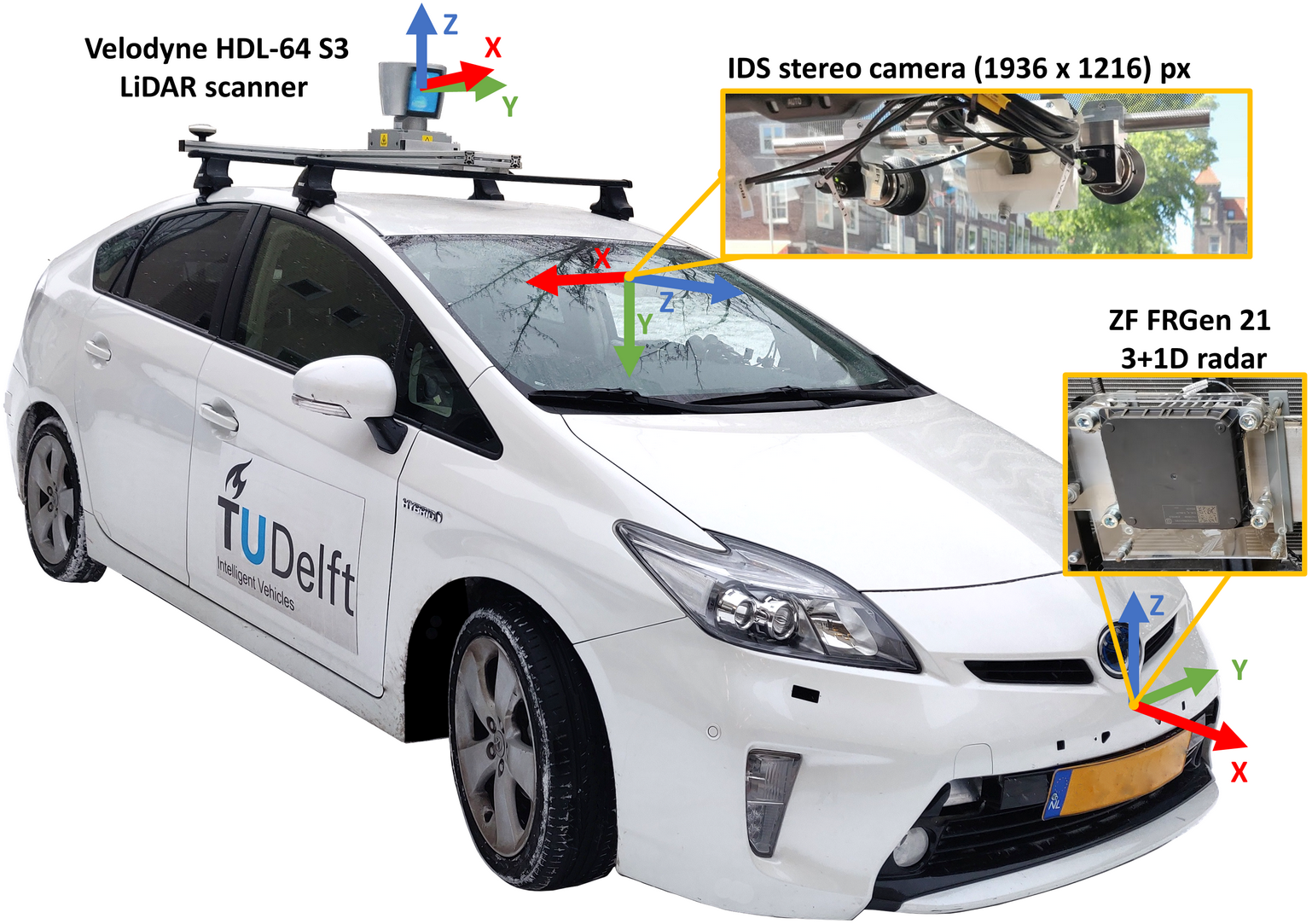
This means, that each of these sensors capture information in their own coordinate system which are located with respect to each other as presented by the 3D plot below:
from vod.visualization import Visualization3D
vis_3d = Visualization3D(frame_data, origin="lidar")
vis_3d.draw_plot(radar_origin_plot=True,
lidar_origin_plot=True,
camera_origin_plot=True,
grid_visible=True,
auto_frame=True)
vis_3d.plot.camera = [5, 5, 3] + \
[0, 0, 0] + \
[0, 0, 1]
Transformations between local coordinate systems¶
When working with the dataset it might be necessary to transform coordinates between the different coordinate systems, for which the information for each sensor and each frame is stored in the calib folder. The FrameTransformMatrix class was created to aid the transformations between the mentioned coordinate systems.
from vod.frame import FrameTransformMatrix
transforms = FrameTransformMatrix(frame_data)
The class contains the homogenous transform matrices as properties, with the following convention: t_target_origin:
- t_camera_lidar: homogeneous transform matrix from the lidar frame, to the camera frame.
- t_camera_radar homogeneous transform matrix from the radar frame, to the camera frame.
- t_lidar_camera: homogeneous transform matrix from the camera frame, to the lidar frame.
- t_radar_camera: homogeneous transform matrix from the camera frame, to the radar frame.
- t_lidar_radar: homogeneous transform matrix from the radar frame, to the lidar frame.
- t_radar_lidar: homogeneous transform matrix from the lidar frame, to the radar frame.
The camera projection matrix is also available using camera_projection_matrix.
print(transforms.t_radar_lidar.round(2))
There are also a number of helper functions included, which can help the transformations:
homogeneous_coordinates: Add description!homogeneous_transformation:project_3d_to_2d:
from vod.frame import homogeneous_transformation
import numpy as np
coordinate = np.array([[0, 0, 0, 1]])
print(homogeneous_transformation(coordinate, transforms.t_radar_lidar).round(2))
Transformation to world coordinates¶
There are three available world transformations in the FrameTransformMatrix class:
- map-camera: global coordinate system.
- odom-camera: local coordinate system.
- UTM-camera: official UTM coordinate system.
The example below shows how the transform can be used, as well as how the coordinates can be plotted to an aerial map.
coordinate = np.array([[0, 0, 0, 1]])
utm_coordinates = homogeneous_transformation(coordinate, transforms.t_utm_camera).T
print(utm_coordinates)
from pdok_wms_request import AerialMapRetriever, CoordTransformer
from pyproj import Transformer, Proj
myProj = Proj(proj='utm',zone=31, ellps='WGS84', preserve_units=False)
lon, lat = myProj(utm_coordinates[0,0], utm_coordinates[1,0], inverse=True)
centre = [lon, lat]
wh_in_m = True
width = 70
height = 70
server_url = "https://service.pdok.nl/hwh/luchtfotorgb/wms/v1_0?SERVICE=WMS&VERSION=1.3.0&REQUEST=GetMap&FORMAT=image/png&TRANSPARENT=true&LAYERS=Actueel_orthoHR&STYLES=&CRS=EPSG:28992"
resolution = 0.
map_retriever = AerialMapRetriever(server_url, resolution=resolution)
map_from_centre = map_retriever.get_map_from_centre(centre, width, height, resolution=resolution, wh_in_m=wh_in_m)
map_from_centre.show(mark_center=True)